Table of Contents
Reducing Energy Consumption in HVAC systems has become one of the most critical priorities for homeowners, businesses, and facility managers in today’s energy-conscious world. Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems are among the largest energy users in any building, often accounting for 40–60% of total Energy Consumption in both residential and commercial environments. This heavy reliance on HVAC systems means that even small inefficiencies can result in substantial increases in energy usage and operating costs over time.
As global energy prices continue to rise and sustainability regulations become more stringent, managing Energy Consumption is no longer a matter of convenience—it is a necessity. Excessive HVAC energy use not only drives up utility bills but also contributes to higher carbon emissions, increased strain on power grids, and accelerated wear on mechanical components. Without proper optimization, HVAC systems are forced to work harder than necessary, leading to frequent breakdowns and reduced system lifespan.
Fortunately, reducing Energy Consumption does not require compromising indoor comfort or air quality. Advances in HVAC technology, combined with smarter operational strategies, make it possible to maintain consistent temperatures while significantly lowering energy use. High-efficiency equipment, intelligent controls, and data-driven maintenance practices allow HVAC systems to deliver optimal performance with minimal wasted energy.
Proactive system management plays a vital role in controlling Energy Consumption. Regular maintenance, proper system sizing, and improved building insulation all help HVAC equipment operate at peak efficiency. When systems are clean, well-calibrated, and supported by energy-efficient building envelopes, they require less energy to achieve the same level of comfort. This translates into lower monthly expenses and improved long-term reliability. hultrafil
In addition, modern HVAC solutions offer advanced monitoring capabilities that provide real-time insights into Energy Consumption patterns. These tools enable homeowners and facility managers to identify inefficiencies, adjust operating schedules, and make informed decisions that reduce unnecessary energy use. Over time, these incremental improvements add up to substantial energy savings.
By adopting the right combination of strategies, it is possible to dramatically reduce Energy Consumption while enhancing comfort, sustainability, and operational efficiency. The following eight proven methods outline practical, effective ways to optimize HVAC performance, lower energy demands, and ensure long-term cost savings—without sacrificing the indoor environments people rely on every day.
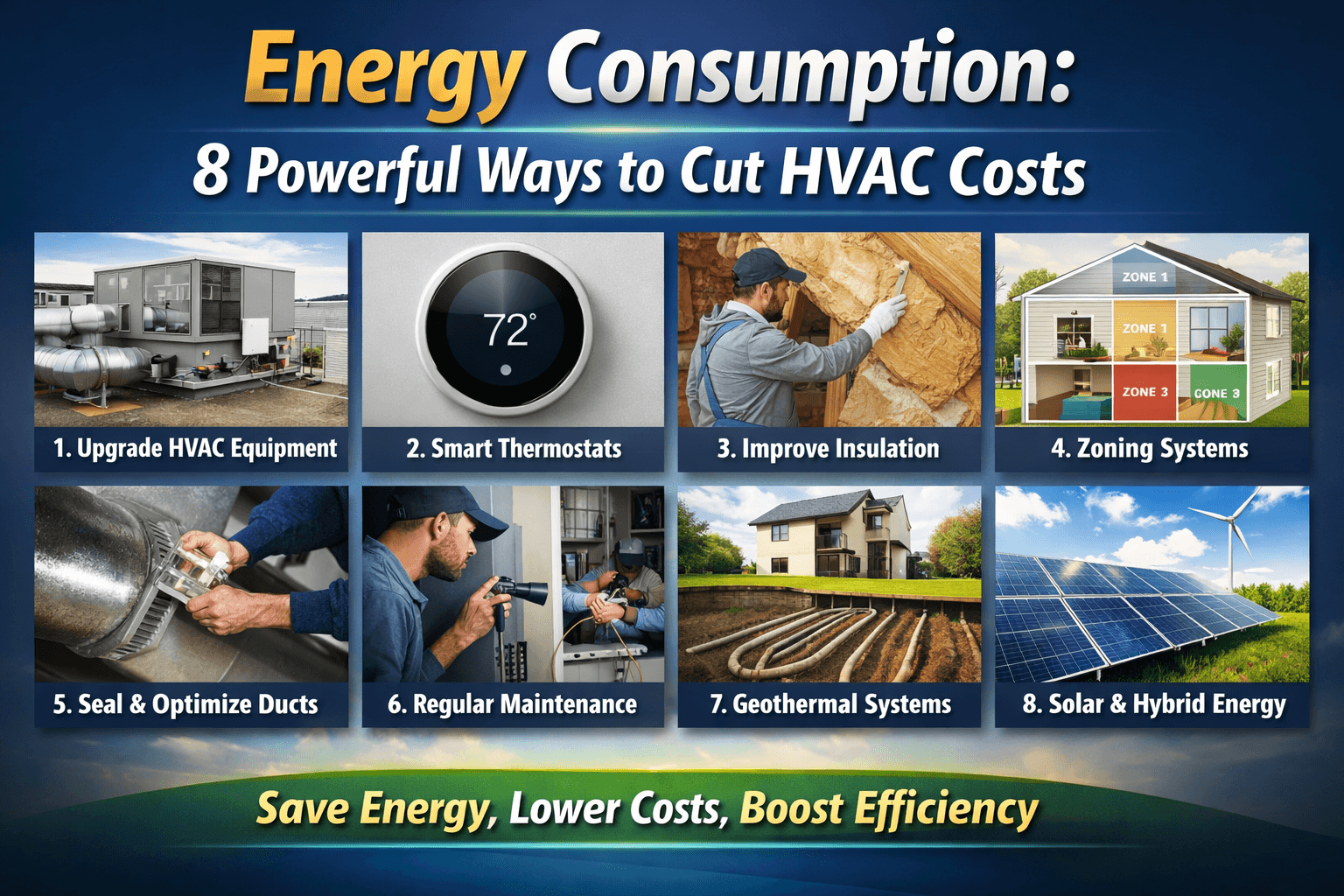
Part 1: Why Reducing Energy Consumption in HVAC Systems Matters
Reducing Energy Consumption in HVAC systems has become a critical concern for homeowners, businesses, and facility managers as energy efficiency moves to the forefront of modern building design and operation. Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems are essential for maintaining indoor comfort, but they are also among the most energy-intensive systems in any building. In many residential and commercial properties, HVAC systems are responsible for 40–60% of total Energy Consumption, making them a primary target for efficiency improvements. fiveable.me
As energy prices continue to rise globally, uncontrolled Energy Consumption can place a significant financial burden on households and organizations alike. Inefficient HVAC operation leads to higher monthly utility bills, unpredictable operating costs, and reduced budget flexibility. For businesses and large facilities, excessive energy use can erode profit margins and increase long-term operational risks. Addressing HVAC-related Energy Consumption is therefore not only an environmental responsibility but also a strategic financial decision.
Beyond cost considerations, high Energy Consumption has a direct impact on environmental sustainability. HVAC systems that rely heavily on fossil fuels contribute to increased greenhouse gas emissions and higher overall carbon footprints. Governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly implementing stricter energy-efficiency standards, making it essential for building owners to proactively manage Energy Consumption to remain compliant and environmentally responsible.
Another often overlooked consequence of excessive Energy Consumption is its effect on HVAC system durability. When systems operate inefficiently, they are forced to run longer cycles and at higher loads, accelerating wear and tear on critical components. This leads to more frequent breakdowns, higher maintenance costs, and a shorter equipment lifespan. By reducing Energy Consumption, HVAC systems can operate more smoothly, reliably, and efficiently over time.
Importantly, lowering Energy Consumption does not mean sacrificing indoor comfort or air quality. Modern HVAC technologies and smart control systems allow precise temperature regulation, balanced airflow, and improved humidity control while using less energy. When HVAC systems are properly designed, maintained, and optimized, they can deliver superior comfort with significantly reduced energy demands.hultrafil
Understanding the importance of Energy Consumption in HVAC systems is the first step toward meaningful improvement. By recognizing how energy is used—and often wasted—building owners and facility managers can make informed decisions that lead to long-term savings, improved performance, and a more sustainable built environment. This foundation sets the stage for the practical strategies that follow, each designed to reduce Energy Consumption without compromising comfort or reliability.
Part 2: Upgrading to Energy-Efficient HVAC Equipment
One of the most impactful steps toward reducing Energy Consumption in HVAC systems is upgrading to modern, energy-efficient equipment. Many homes and commercial buildings still rely on aging HVAC units that were designed before today’s efficiency standards existed. These older systems typically require far more energy to produce the same heating or cooling output, resulting in unnecessarily high Energy Consumption and rising operational costs.
Advancements in HVAC technology have dramatically improved system efficiency over the past decade. Modern systems are engineered with high-performance compressors, variable-speed motors, and advanced heat exchangers that adjust output based on real-time demand. Unlike traditional systems that operate at full capacity regardless of need, energy-efficient HVAC units modulate performance, significantly reducing Energy Consumption during partial load conditions.hultrafil
Efficiency ratings play a crucial role in understanding potential energy savings. Metrics such as SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio), EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio), and AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) provide clear indicators of how effectively a system converts energy into heating or cooling. Higher ratings directly correlate with lower Energy Consumption, making them an essential consideration when selecting new equipment.
Upgrading HVAC equipment also improves system compatibility with smart technologies that further reduce Energy Consumption. Many modern units integrate seamlessly with smart thermostats, zoning systems, and building management platforms. These integrations enable precise control over temperature settings, occupancy schedules, and system output, eliminating wasteful energy use while maintaining optimal comfort levels. fiveable.me
Although the initial investment in energy-efficient HVAC equipment may appear substantial, the long-term benefits often outweigh the upfront costs. Reduced Energy Consumption leads to lower utility bills, fewer maintenance issues, and extended equipment lifespan. In many cases, energy savings alone can offset the cost of replacement within a few years, especially in high-usage commercial environments.
In addition, upgrading HVAC systems may qualify property owners for energy rebates, tax incentives, or sustainability certifications, further improving the financial return while supporting environmental goals. By lowering Energy Consumption, efficient HVAC equipment helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and aligns buildings with evolving energy regulations.
Ultimately, upgrading to energy-efficient HVAC systems is not just a technical improvement—it is a strategic investment. By modernizing equipment, building owners take a decisive step toward long-term Energy Consumption reduction, improved system reliability, and a more sustainable approach to indoor climate control.
Discover more : 8 Energy-Efficient Cooling Systems That Can Transform Your Home Comfort
Part 3: Performing Regular HVAC Maintenance to Reduce Energy Consumption
Regular maintenance is one of the most effective ways to minimize Energy Consumption in HVAC systems. Even the most advanced, energy-efficient equipment can lose its effectiveness if not properly maintained. Dust, debris, worn components, and minor system malfunctions can significantly increase the amount of energy required to heat or cool a building, resulting in higher Energy Consumption and elevated utility costs.hultrafil
Routine maintenance ensures that HVAC systems operate at peak performance, reducing unnecessary energy use and extending the lifespan of the equipment. Key maintenance tasks that directly impact Energy Consumption include:
- Replacing or Cleaning Air Filters: Dirty air filters restrict airflow, forcing the system to work harder to maintain desired temperatures. This not only increases Energy Consumption but also puts strain on fans and compressors. Replacing filters regularly can reduce energy usage and improve indoor air quality.
- Inspecting and Cleaning Coils: Evaporator and condenser coils are essential for efficient heat transfer. Over time, dust and grime accumulate on these surfaces, reducing system efficiency. Clean coils enable the HVAC system to operate smoothly, directly lowering Energy Consumption.
- Checking Refrigerant Levels: Incorrect refrigerant charge or leaks can drastically increase the workload on compressors, leading to higher energy use. Ensuring proper refrigerant levels maintains optimal efficiency and keeps Energy Consumption in check.
- Lubricating Moving Parts: Components like motors, fans, and bearings require proper lubrication to reduce friction. Neglecting lubrication increases mechanical resistance, causing the system to consume more energy.hultrafil
- Inspecting Ductwork and Airflow: Leaks or blockages in ductwork can waste up to 30% of conditioned air, dramatically increasing Energy Consumption. Regular inspection and sealing of ducts ensure efficient airflow and optimal system performance.
- Testing Thermostat and Controls: Malfunctioning thermostats or control systems can cause HVAC equipment to run unnecessarily, driving up energy usage. Regular testing and calibration maintain precise control and prevent wasted energy.
Consistently performing these maintenance tasks can reduce HVAC-related Energy Consumption by as much as 15–20%, depending on the age and condition of the system. Beyond energy savings, routine maintenance also prevents costly breakdowns, ensures consistent indoor comfort, and prolongs equipment life.
Additionally, a proactive maintenance approach allows facility managers and homeowners to identify inefficiencies before they escalate. For example, minor issues such as a small refrigerant leak or a slightly clogged coil may seem insignificant, but over time, they can lead to substantial increases in Energy Consumption and higher repair costs. By addressing these problems early, maintenance not only saves energy but also prevents expensive emergency repairs.
In summary, regular HVAC maintenance is a cornerstone of energy efficiency. It ensures that systems operate as designed, minimizes wasted energy, and maximizes comfort, all while reducing overall Energy Consumption and environmental impact.
Part 4: Optimizing Thermostat Settings and Scheduling to Lower Energy Consumption
One of the simplest yet most effective ways to reduce Energy Consumption in HVAC systems is through intelligent thermostat management. Many buildings waste significant energy simply because heating or cooling is applied when it isn’t needed, or because systems operate at higher capacity than necessary. Proper thermostat use and scheduling can dramatically cut energy waste while maintaining indoor comfort.hultrafil
1. Programmable Thermostats
Installing a programmable thermostat allows you to set temperature schedules based on occupancy patterns. For example, in residential homes, temperatures can be slightly lowered during the night or when the house is empty, then restored before occupants return. Similarly, in commercial buildings, HVAC systems can be reduced during nights or weekends when offices are unoccupied. By tailoring HVAC operation to actual usage, programmable thermostats significantly reduce unnecessary Energy Consumption.
2. Smart Thermostats
Smart thermostats take scheduling a step further by using artificial intelligence, sensors, and Wi-Fi connectivity to automatically adjust temperatures. These devices can learn daily routines, detect when rooms are unoccupied, and even respond to local weather conditions. By continuously optimizing system performance, smart thermostats help maintain comfort while minimizing Energy Consumption.
3. Zoning Controls
Thermostat zoning allows different areas of a building to be heated or cooled independently. Instead of conditioning the entire building to the same temperature, zoning systems direct airflow only where it is needed. This targeted approach not only reduces Energy Consumption but also improves comfort, as occupants in different areas can maintain their preferred temperatures. fiveable.me
4. Seasonal Adjustments
Adjusting thermostat settings according to seasonal needs is another simple way to lower Energy Consumption. During winter, setting temperatures slightly lower can reduce heating demand, while in summer, raising temperatures slightly decreases cooling requirements. Even small changes of 1–2 degrees can have a measurable impact on overall energy use without noticeably affecting comfort.
5. Regular Monitoring and Adjustment
Even with programmable or smart thermostats, periodic review of settings is essential. Building usage patterns may change over time, and failing to update schedules can result in wasted energy. Monitoring energy reports or system logs allows building managers or homeowners to identify unnecessary HVAC activity and reduce Energy Consumption.
By implementing these thermostat strategies, it is possible to achieve significant reductions in Energy Consumption—often between 10% and 25% annually—without making major changes to the HVAC system itself. Optimizing thermostat settings is a cost-effective, low-effort method to ensure that your HVAC system operates efficiently while maintaining comfort in every room. hultrafil
In conclusion, intelligent thermostat management is not just about convenience—it is a powerful tool for reducing energy waste. When combined with other energy-saving strategies, it helps maximize the efficiency of HVAC systems, lower utility bills, and minimize environmental impact, all while maintaining the indoor comfort that occupants rely on daily.
Part 5: Improving Building Insulation and Sealing to Reduce Energy Consumption
While HVAC equipment plays a critical role in maintaining indoor comfort, the efficiency of the system is heavily influenced by the building itself. Poor insulation and air leaks can force even the most advanced HVAC systems to work harder than necessary, dramatically increasing Energy Consumption. Improving insulation and sealing gaps is a highly effective way to reduce energy use while maintaining a consistent and comfortable indoor environment.hultrafil
1. The Role of Insulation in Energy Consumption
Insulation acts as a thermal barrier, slowing the transfer of heat between indoor and outdoor spaces. In the winter, proper insulation keeps warm air inside, reducing the heating load on HVAC systems. In the summer, insulation helps prevent unwanted heat from entering, decreasing the cooling demand. Without adequate insulation, HVAC systems run longer and consume more energy, leading to higher Energy Consumption and increased utility costs.
Walls, roofs, floors, and attics are all critical areas where insulation improvements can make a significant difference. Modern insulation materials, such as spray foam, rigid panels, or high-performance fiberglass, provide excellent thermal resistance and can dramatically reduce HVAC workload. By enhancing these areas, buildings can maintain stable indoor temperatures with less energy, directly lowering Energy Consumption. fiveable.me
2. Sealing Air Leaks
Even well-insulated buildings can lose energy through air leaks around windows, doors, vents, and ductwork. These leaks allow conditioned air to escape and outdoor air to enter, forcing HVAC systems to work harder to maintain desired temperatures. Sealing these gaps with weatherstripping, caulking, or specialized sealants reduces energy waste and lowers Energy Consumption.
Ductwork is another common source of energy loss. Leaks, loose connections, and poor insulation can cause up to 30% of heated or cooled air to escape before reaching its intended destination. Inspecting, sealing, and insulating ducts ensures that conditioned air is delivered efficiently, helping to reduce Energy Consumption and improve overall system performance.
3. Windows and Doors
Upgrading to energy-efficient windows and doors with proper seals can significantly reduce Energy Consumption. Double or triple-pane windows with low-emissivity coatings minimize heat transfer, keeping indoor temperatures stable and reducing HVAC demand. Even simple improvements, such as adding weatherstripping or thermal curtains, can prevent energy loss and reduce the workload on HVAC systems.hultrafil
4. Attic and Roof Improvements
Heat tends to rise, making attics and roofs a major source of energy loss. Adding insulation in attics and ensuring proper ventilation can prevent heat from escaping in the winter or entering in the summer. Properly insulated and ventilated attics reduce HVAC runtime, lower Energy Consumption, and enhance indoor comfort.
By addressing insulation and sealing issues, building owners can achieve a substantial reduction in Energy Consumption—often between 15% and 30%, depending on the condition of the building envelope. These improvements not only lower energy costs but also contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly building.
Improving insulation and sealing gaps is a fundamental strategy for reducing Energy Consumption in HVAC systems. By minimizing heat loss, preventing air leaks, and optimizing the building envelope, HVAC systems operate more efficiently, consume less energy, and maintain consistent indoor comfort. When combined with other energy-saving measures, such as upgrading equipment and optimizing thermostat settings, these improvements play a critical role in creating energy-efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable buildings.
Part 6: Using Zoning Systems for Targeted Comfort to Reduce Energy Consumption
Another highly effective method to reduce Energy Consumption in HVAC systems is the implementation of zoning systems. Traditional HVAC setups often operate at a uniform temperature throughout the building, regardless of whether all areas are occupied or require conditioning. This one-size-fits-all approach can lead to significant energy waste, as HVAC systems expend energy cooling or heating spaces unnecessarily. Zoning systems provide a smarter, more efficient solution.
1. What Zoning Systems Do
Zoning systems divide a building into separate areas, or “zones,” each with its own thermostat or control point. Dampers in the ductwork regulate airflow to these zones, ensuring that only the areas that require heating or cooling receive conditioned air. For example, unoccupied rooms, storage areas, or seldom-used offices do not consume energy unnecessarily, reducing overall Energy Consumption. fiveable.me
2. Benefits of Targeted Comfort
By directing conditioned air only where it is needed, zoning systems improve comfort and lower energy costs. Occupants can set different temperatures for different rooms based on preferences, usage patterns, or time of day. This targeted approach allows HVAC systems to operate more efficiently, significantly reducing Energy Consumption without sacrificing comfort.
3. Integration with Smart Controls
Modern zoning systems often integrate seamlessly with smart thermostats and building management systems. This integration allows for automated adjustments based on occupancy sensors, schedules, or even remote control via mobile apps. By fine-tuning airflow and system output, smart zoning systems can optimize HVAC operation and minimize energy waste, further lowering Energy Consumption.
4. Cost and Energy Savings
While the installation of zoning systems requires an upfront investment, the long-term energy savings and improved comfort make it worthwhile. Studies have shown that properly designed zoning systems can reduce Energy Consumption by 10–30%, depending on building size, occupancy patterns, and existing HVAC efficiency. In addition to energy savings, zoning reduces wear and tear on HVAC components by preventing unnecessary cycles, extending system lifespan.hultrafil
5. Ideal Applications
Zoning is particularly beneficial in large homes, multi-story buildings, and commercial facilities where temperature requirements vary by zone. Areas such as basements, attics, conference rooms, or individual office spaces often have unique heating or cooling needs. Zoning ensures that energy is only used where it is truly needed, maximizing efficiency and comfort simultaneously.
Zoning systems are a practical and effective strategy for reducing Energy Consumption while enhancing comfort. By delivering conditioned air selectively, minimizing waste, and integrating with smart controls, zoning systems optimize HVAC operation across the building. When combined with other energy-saving measures, such as upgrading equipment and improving insulation, zoning contributes to a holistic approach for reducing energy use and creating sustainable, cost-efficient buildings. fiveable.me
Part 7: Upgrading Ductwork and Air Distribution Systems to Minimize Energy Consumption
While HVAC equipment and controls are critical to efficiency, the performance of a system is only as good as the ductwork and air distribution infrastructure that delivers conditioned air throughout a building. Poorly designed or deteriorating duct systems can significantly increase Energy Consumption, as the HVAC unit must work harder to maintain consistent indoor temperatures. Upgrading and optimizing ductwork is therefore a vital strategy for reducing energy waste and improving system efficiency.
1. How Ductwork Impacts Energy Consumption
Air leaks, poorly sized ducts, and inefficient layouts force HVAC systems to compensate for lost airflow, increasing runtime and energy use. Research indicates that up to 30% of conditioned air can be lost through leaky or inefficient duct systems, resulting in unnecessarily high Energy Consumption. This not only increases utility bills but also causes uneven heating and cooling, making some areas uncomfortable despite the system running at full capacity.
2. Inspecting and Sealing Ducts
Regular inspection of ductwork is essential to identify leaks, loose connections, or blockages. Sealing ducts with mastic or metal-backed tape ensures that conditioned air reaches its intended destination, reducing wasted energy. By minimizing air loss, sealing can directly lower Energy Consumption and improve system responsiveness.
3. Insulating Ductwork
Duct insulation plays a critical role in maintaining the temperature of conditioned air as it travels through walls, ceilings, and unconditioned spaces. Uninsulated or poorly insulated ducts can lose heat in winter and gain heat in summer, forcing HVAC units to work harder and increasing Energy Consumption. Adding proper insulation reduces energy loss, improves comfort, and lowers the workload on heating and cooling equipment.hultrafil
4. Redesigning for Efficiency
In some cases, existing duct layouts may be inefficient, with long runs, sharp bends, or undersized sections that restrict airflow. Redesigning or resizing ducts can improve airflow balance, reduce pressure drops, and minimize the energy required to deliver conditioned air throughout the building. This optimization directly reduces Energy Consumption while enhancing comfort in all areas of the space.
5. Integrating with Modern HVAC Systems
Upgraded ductwork works best when combined with energy-efficient HVAC equipment and smart controls. Properly sealed and insulated ducts allow variable-speed systems, zoning controls, and smart thermostats to operate as intended, maximizing efficiency and reducing Energy Consumption. Conversely, even the most advanced systems cannot perform optimally if ducts are leaky or poorly designed.
Upgrading and optimizing ductwork is a crucial strategy for lowering Energy Consumption in HVAC systems. From sealing leaks and insulating ducts to redesigning layouts for improved airflow, every improvement reduces energy waste, lowers utility costs, and enhances overall comfort. When implemented alongside equipment upgrades, thermostat optimization, and building envelope improvements, ductwork enhancements form a key component of a comprehensive energy-efficiency strategy for any residential or commercial property. fiveable.me
Part 8: Integrating Renewable Energy and Hybrid Systems to Reduce Energy Consumption
As energy efficiency becomes a priority, integrating renewable energy sources and hybrid HVAC systems offers one of the most advanced ways to reduce Energy Consumption. Traditional HVAC systems rely heavily on electricity or fossil fuels, which not only increase energy costs but also contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. By incorporating renewable energy technologies, building owners can significantly lower Energy Consumption while improving sustainability and reducing operational costs.
1. Solar-Assisted HVAC Systems
Solar-assisted HVAC systems use solar energy to supplement heating, cooling, or hot water generation. For instance, solar thermal panels can preheat water or provide supplementary heat to reduce the demand on conventional systems. By relying partially on renewable energy, these systems reduce the overall Energy Consumption of the HVAC system while decreasing reliance on grid electricity or fossil fuels.
2. Hybrid Heating and Cooling Systems
Hybrid systems combine traditional HVAC units with high-efficiency, renewable-based components. For example, a hybrid heat pump system can switch between electric and gas heating depending on efficiency and energy costs. This approach optimizes energy use, ensuring that the system always operates in the most efficient mode, thereby minimizing Energy Consumption.
3. Geothermal HVAC Systems
Geothermal systems use the stable temperature of the earth to heat and cool buildings. By tapping into underground thermal energy, these systems can provide heating and cooling with far less energy than conventional HVAC systems, significantly reducing Energy Consumption. While installation costs can be higher initially, geothermal systems often pay for themselves over time through energy savings. fiveable.me
4. Energy Storage and Smart Grid Integration
Combining renewable energy systems with energy storage, such as batteries, allows HVAC systems to store excess energy generated during low-demand periods for later use. Integration with smart grids can further optimize energy use, drawing from renewable sources during peak times and minimizing Energy Consumption from traditional electricity sources.
5. Environmental and Financial Benefits
Integrating renewable energy and hybrid systems reduces both Energy Consumption and environmental impact. Lower energy use translates into decreased greenhouse gas emissions, while reduced reliance on fossil fuels helps protect against rising energy costs. Additionally, many regions offer incentives, tax credits, and rebates for renewable energy installations, improving the financial return on investment.fiveable.me
Incorporating renewable energy and hybrid systems represents the future of energy-efficient HVAC design. These solutions provide a powerful way to reduce Energy Consumption, lower operating costs, and create a sustainable, environmentally responsible building. When combined with strategies such as equipment upgrades, proper maintenance, zoning systems, and improved insulation, renewable integration completes a comprehensive approach to minimizing energy use while maintaining optimal comfort and reliability.
Conclusion
Reducing Energy Consumption in HVAC systems is no longer just a recommendation—it is a necessity for anyone seeking to lower energy costs, improve system performance, and support environmental sustainability. As we have explored in this guide, there are multiple strategies that, when combined, create a comprehensive approach to energy efficiency. From upgrading to high-efficiency HVAC equipment and performing regular maintenance, to optimizing thermostat settings, improving insulation, implementing zoning systems, upgrading ductwork, and integrating renewable energy, each step plays a crucial role in lowering Energy Consumption. fiveable.me
The benefits of reducing Energy Consumption extend far beyond cost savings. Energy-efficient HVAC systems operate more reliably, experience less wear and tear, and provide consistent comfort for occupants. In addition, minimizing energy use helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contributes to a more sustainable future—a goal increasingly important for homeowners, businesses, and building operators alike.
Implementing these strategies does not require sacrificing comfort. Modern technologies, smart controls, and proactive management make it possible to enjoy optimal indoor environments while consuming less energy. By taking deliberate steps to monitor, optimize, and innovate HVAC systems, building owners and managers can achieve long-term reductions in Energy Consumption, lower utility bills, and create resilient, efficient, and environmentally responsible spaces.
In short, controlling Energy Consumption in HVAC systems is a practical, impactful, and achievable goal. The combination of advanced equipment, smart operational practices, and sustainable technologies ensures that comfort and efficiency go hand in hand—allowing buildings to perform better today and for years to come.
Read more : 11 Energy-Saving HVAC Tips Every Homeowner Should Know

